To make smart food choices, it is important to read the labels on the packages of food you buy. The health claims on the front of the package are not always the best place to look. The nutrition facts label will give you more information. Knowing how to read food labels can help you make better choices at the store.
Serving size
The serving size is the amount of food you would need to eat to get the amount of listed nutrients. The servings per container tell how many servings are in the whole package. 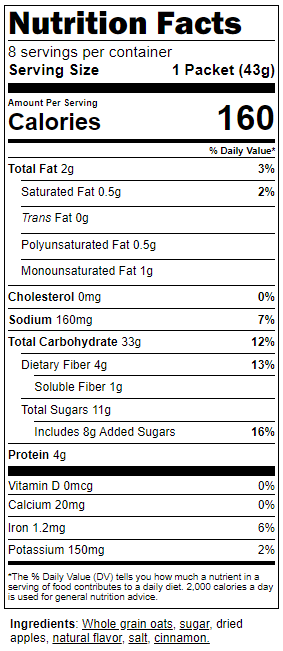
Check calories
Calories are the amount of energy that the food or drink gives you. The total number of calories depends on how many servings you eat. If you ate two servings of this food, the number of calories would double to 320.
Limit saturated and trans fats
Look for foods that have:
- 2 grams of saturated fat
- 2 grams trans fat.
Increase your Fiber
Fiber makes you feel full. Aim for at least 3 grams of fiber in grain foods like cereal, pasta, granola bars, and bread.
Limit Sodium
Choose foods with 15% of the daily value of sodium or less.
Limit added Sugar
- Choose beverages with 3 grams of sugar or less.
- Choose foods with 9 grams if added sugar or less.
Choose whole grains
To help increase fiber, “whole” should be in the first ingredient in grain foods (look for “whole wheat” or “whole grain).
Quick Guide to % of Daily Value (%DV)
- 5% or less is Low
- 20% or more is High
What do the words on the food label mean?
Don’t be fooled by words on the front of a package. Always read the food label.
Here are some of the common terms you may find on a food label:
- Calorie. A unit that tells you how much energy a food gives the body.
- Saturated fat. A fat that is solid at room temperature. It is found in things like butter, cheese, whole milk, ice cream, and meat.
- Trans fat. A liquid fat that is treated (hydrogenated) so it is solid at room temperature. It is in cookies, crackers, fried foods, and processed foods.
- Unsaturated fat. A fat that is liquid at room temperature. It is found in vegetable oils, nuts, and fish. There are 2 kinds: Poly- and Mono-unsaturated.
- Cholesterol. A type of fat your body needs to make vitamin D, some hormones, and other important things. It is in food products such as high-fat dairy products, egg yolks, and high-fat meat. Food cholesterol does not affect body cholesterol.
- Sodium. A component of salt. Almost all foods have sodium in them naturally, but processed foods have a lot of added sodium.
- Total carbohydrate. A combination of many types of carbohydrates: dietary fibers, sugars, and other carbohydrates.
- Protein. A part of food that the body needs to grow, repair itself and build muscle. It can be found in meat, fish, dairy, soy, beans, nuts, and other foods.



