Juvenile Xanthogranuloma (JXG)
What is juvenile xanthogranuloma?
Juvenile Xanthogranuloma (JXG) is a skin condition that is seen in infants and children.
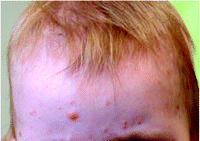
- Yellow bumps form on the skin. The bumps may be as small as a pin head up to as large as a pea. They are often found on the scalp, neck and face. One bump or several bumps may be found.
- If many JXG on the skin, there may also be JXG in the eye.
- JXG can sometimes be seen at birth. Other times the bumps can form after birth for up to 1 to 2 years.
- The bumps normally go away on their own in children over 3 to 6 years.
What causes JXG?
It is not clear what causes JXG to appear. At times it has been seen with other conditions such as neurofibromatosis. The doctor or nurse will explain more about what causes JXG.
How is JXG diagnosed?
JXG is often diagnosed by what the bumps look like. A small piece of affected skin may be removed after the area has been numbed by a local anesthetic. This is called a skin biopsy. It may be needed to make the correct diagnosis.
How is JXG treated?
The bumps will often go away with no treatment. Sometimes treatment is needed. Treatment depends on the size and the location of the bumps. The doctor or nurse will talk with you if treatment is needed for your child. If your child has many JXG on the skin, your doctor may ask you to see an eye doctor (ophthalmologist) to check the eyes for JXG.



