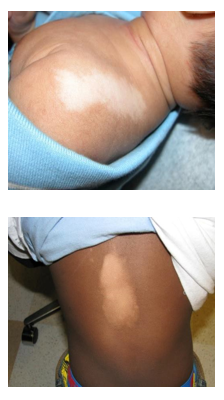
What is vitiligo?
Loss of skin color is called vitiligo. It can happen on any part of the body, but is most common on the hands, forearms, feet or face. Vitiligo may start at any age and can affect anyone. It is easier to see in people with darker skin.
Vitiligo may look like:
- A few spots that lighten or turn completely white.
- Large patches of skin color loss.
What causes it?
The exact cause is not known. Vitiligo can develop when cells are destroyed by the body’s immune system. These cells make the skin color, called pigment. When the cells die, they no longer make pigment. This can cause an area of skin or hair
to turn white.
How is it diagnosed?
Vitiligo is most often diagnosed by a physical exam. If it is hard to tell the areas of vitiligo from normal skin, a special exam may be done. This exam is done in a dark room under a special light, called a Wood’s light.
How will it affect my child?
The more common types of vitiligo are:
Generalized. This is the most common. White areas can be seen on the face, lips, hands, arms, legs, or genitals. Skin can improve on its own, but will always be somewhat lighter. Sometimes the skin will not return to its original color.
Segmental. This type affects only one part of the body, such as an arm or a leg. Segmental vitiligo tends to progress for a year or two, and then stop spreading. It is less likely to improve on its own.
People with vitiligo should avoid sun exposure and tanning. Areas of skin with vitiligo sunburn very easily. Sometimes the sun will add some color to the skin, but this does not last and may only happen is some areas. Vitiligo is harder to see on a light-skinned person. Tanning makes the normal skin darker, which make the vitiligo easier to see. Sunscreen should always be used to protect from sunburn.
How is it treated?
Sometimes, skin color comes back without treatment as small, freckle-like spots. Other times pigment will continue to be lost in large patches. Treatment can be helpful in many cases, but not always. Children tend to have better results than adults.
- Phototherapy (NB-UVB). This therapy uses light to get color back into the skin. Therapy requires two to three treatment sessions per week for several months.
- Creams and ointments. Medicine, such as topical corticosteroids is put on the skin. It can be used to get color back in small areas.
- When vitiligo treatment does not work well, areas with loss of skin color may be covered with makeup (Dermablend®) or self-tanner. Ask your doctor what you should use.