Beta Thalassemia Trait
What is Beta Thalassemia?
- Beta thalassemia is a blood disorder. It changes hemoglobin in the red blood cells.
- Hemoglobin is a protein in the red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to all parts of the body.
What does Beta Thalassemia Trait mean?
It means there is one gene in your body for thalassemia. This is a change in your gene that makes hemoglobin.
In order to have the disease, you must have 2 genes for beta thalassemia. You do not have the disease. You will not get it later in life.
What are genes?
Genes are the codes for how to make all the parts of the body. Every person has 2 sets of genes. One set came from the egg and one set came from the sperm.
How does Beta Thalassemia trait affect people?
- People with beta thalassemia trait have both normal and abnormal hemoglobin in the red blood cells. This causes the body to make less hemoglobin. Low amounts of hemoglobin is called
anemia. People with beta thalassemia trait may always have mild anemia. This kind of anemia is often confused with anemia that is caused by low iron. - People with beta thalassemia trait can pass the trait to their children.
- More than 2 million people in the US have Beta thalassemia trait. It is most common in people who come from:
- Africa
- Mediterranean
- Asia
- Middle East
Why is it important to get tested?
It is important to know if you have beta thalassemia trait.
- Patients with beta thalassemia trait should have their iron levels checked before they start taking iron.
- Finding out that a person has the beta thalassemia trait can help find other family members who also have it.
- When two people both have the trait, their children could be born with beta thalassemia disease. Beta thalassemia disease is serious and needs lifelong medical care.
If both parents have the trait, with each pregnancy:
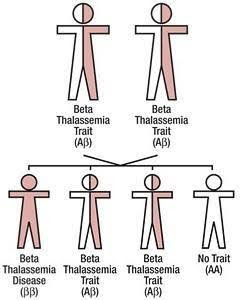
| Chance: | The Child: |
| 1 out of 4 (25%) | could have the disease. |
| 2 out of 4 (50%) | could have the trait, not the disease. |
| 1 out of 4 (25%) | could have normal hemoglobin |
If only one parent has the trait and the other does not, with each pregnancy:
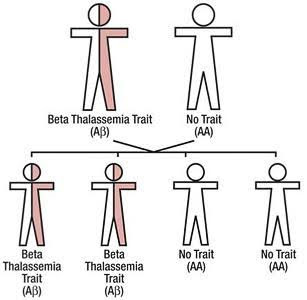
- None of the children will have beta thalassemia disease.
- There is a 2 out of 4 (50%) chance that a child will have beta thalassemia trait.
If one parent has beta thalassemia trait and the other parent has sickle cell trait, there is a chance their children could have sickle cell disease. This is also
serious. The child will need lifelong medical care.



