Sickle Cell Disease: Acute Chest Syndrome
Jump to:
What is acute chest syndrome? 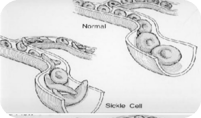
Acute chest syndrome occurs when the red blood cells sickle and stick together in the lungs. This does not let enough blood and oxygen get to the lungs. This can cause tissue damage. Acute chest syndrome may be triggered by a lung infection such as pneumonia. It may also be caused by asthma that is not controlled. It can occur before, during or after a sickle cell pain episode.
What are the symptoms?
There may be one or more of these symptoms:
- Fast breathing or trouble breathing.
- Chest, stomach (abdomen) or back pain along with the breathing problems.
- Fever.
- Congested cough.
If any of these symptoms happen go to the Emergency room within one hour.
What happens in the hospital?
- Oxygen and antibiotics will most likely be given.
- Your child may need a blood transfusion to help breathing to get better.
- Pain medicine will be given.
- It is important to get out of bed several times a day to sit in a chair or walk. This will help with deep breathing.
- Your child will need to use an Incentive Spirometer. This is a device that helps them take deeper breaths.



