Retinoblastoma: Looking at the Tumor
Ways To Look at the Tumor
There are different ways or tests your provider may use to look at your child’s retinoblastoma tumor. These will help provide the team with the most accurate information. These may be done when your child is diagnosed. They also can be done during and after treatment. This allows the provider to compare the tumor and how it changes over time.
All These Tests Are Done:
- In the operating room.
- While your child is asleep. Your child will be given medicine to help them be asleep during the test.
- After giving your child eye drop medicine. This medicine dilates or makes the pupil bigger. This allows the provider to get a better view of the retina.
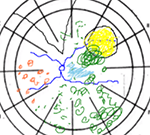
Fundus Drawings
With this test, the provider will make a drawing of the inner eye. Different colors are used to show the parts of the eye, including the tumor. This allows them to document how the retina of the eye looks. They can also make notes about the retina.
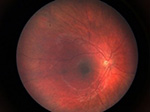
Digital Retinal Photographs
With this test, the provider will take digital images of the retina.
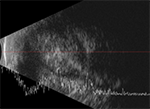
Ultrasound
With this test, the provider will use ultrasound or sound waves to look inside the eye. This helps to measure the size of the tumor.
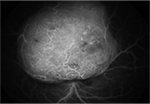
Fluorescein Angiography
With this test, the provider will look at the way blood flows in the retina.
- Your child will have an IV placed.
- A special dye (fluorescein) will be put into your child’s IV. The dye is bright yellow. It can cause your child’s skin to look yellow for a few hours. The dye will also cause your child’s urine to be bright yellow for 1 to 2 days.
- The dye travels through the blood stream into the blood vessels of the retina.
- As the dye goes through these blood vessels a camera will take many pictures very quickly.
A very small number of patients can have side effects from this test. These may include:
- Upset stomach
- Headache
- Dizziness or fainting
- Hives or itching
A smaller number of patients could have trouble breathing or an anaphylactic reaction.