In this section
Pilonidal cysts and abscesses
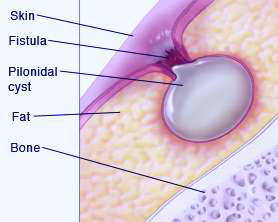
Pilonidal means “nest of hair”. A pilonidal cyst is an abnormal sac that develops at the top of the buttocks, near the split (cleft). The sac contains skin and ingrown hairs. If the cyst gets infected, it is called a pilonidal abscess. It is most common in the teenage years and early twenties.
What causes a cyst to form?
While the exact cause of pilonial cysts is debated. It most commonly occurs in people 10-30 years of age, is more common in males and more common in people with more hair in that region. Most people believe that it related to Hormone changes, Hair growth, wearing Tight fitting clothes rubbing on the skin and Sitting for long periods of time.
What are the symptoms of a pilonidal cysts?
Most cysts will present as a mass at the top of the crease in the buttocks. It may cause mild pain and may cause a small amount of blood tinged drainage. It may look like there are several small pits in the skin. For many people this will go unnoticed until an infection occurs.
What are the symptoms of an abscess?
When a pilonidal cyst becomes infected it is typically very painful over a mass at the top of the crease in the buttock. Most commonly the skin will be red and very tender to touch. Most people have a hard time sitting as a result of the pain. They may also experience drainage and fevers.
How is the abscess treated?
Early treatment may include sitting in a tub of warm water. This may decrease the pain. It may also help the abscess drain. An antibiotic may also be given.
If the abscess gets worse, surgery may be needed. The surgery is called an Incision and Drainage (I & D). It allows the pus to drain out, which will decrease the pain. Antibiotics may be prescribed after the surgery.
How are Pilonidal Cysts treated when there is no infection?
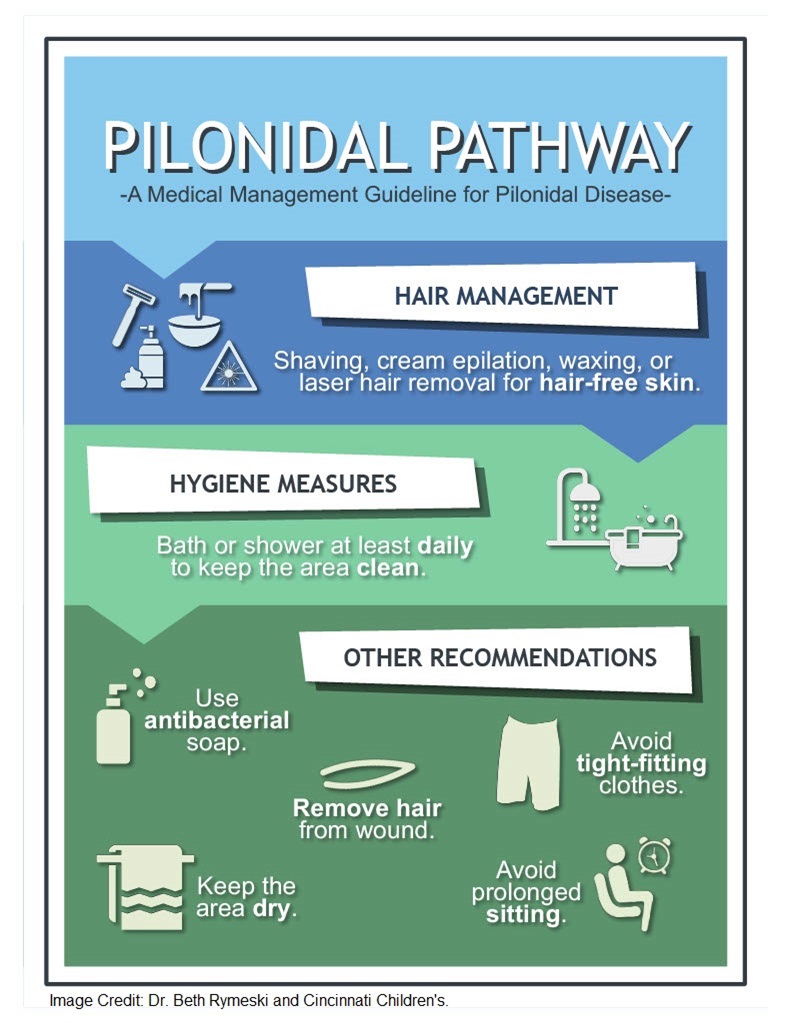
Non-surgical treatment: Patients who do not have active symptoms, non-surgical treatment is a reasonable option. Good hygiene is very important. We recommend showering every day and using an antibacterial soap. The area should be kept clean and dry. Avoiding sitting for long periods of time and tight fitting clothes. Most importantly we recommend keeping the area free of hair. There are several options for this including shaving, using depilatory creams .or electrolysis or having laser hair removal done.
Surgical treatment
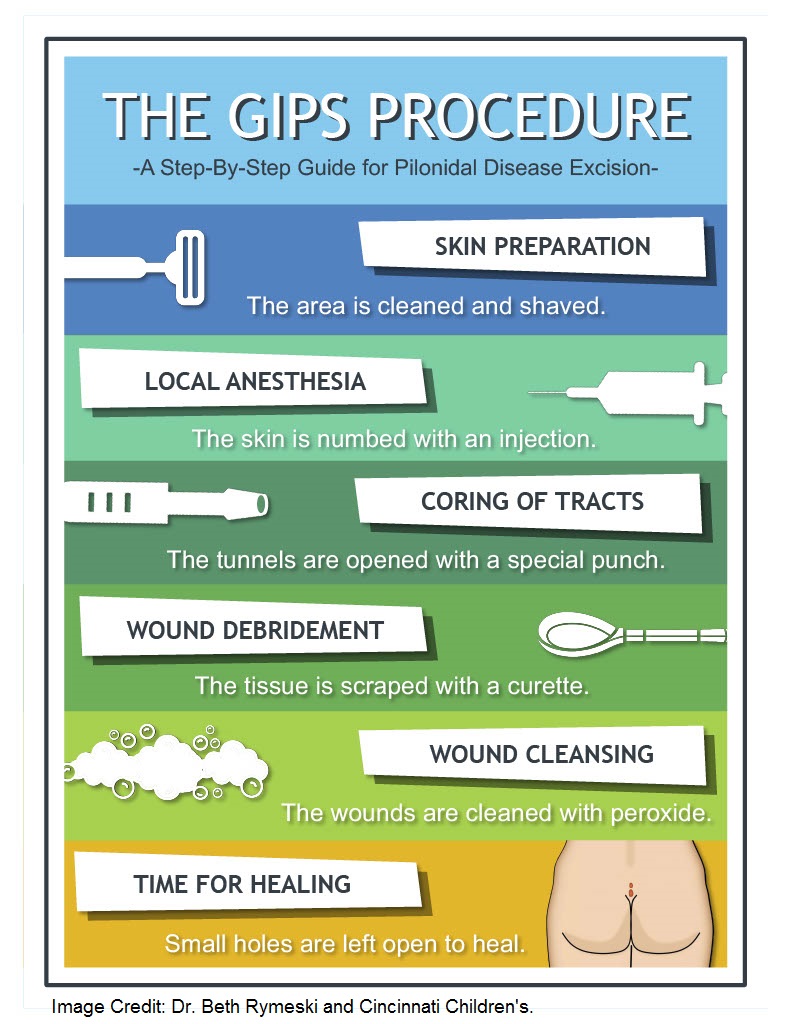
While surgery is helpful for many patients, it can be complicated by problems with wound healing, infections and recurrence of the pilonidal disease. For this reason we don’t always recommend surgery as the first line of treatment. However, in patients who have continuous drainage, pain or recurrent infections despite non-surgical treatment, surgical treatment is often recommended. There are several different surgery options. The most common are some type of surgery the completely removes the involved area. Some surgeons have recommended that the wound be left open to heal over several weeks while others have used flap closure to rotate in normal skin. One of the more recent surgical techniques that minimizes these complications is called the GIPS procedure. GIPS is felt to be a less invasive surgery since it avoids larger incisions. Instead, GIPS surgery involves uses small (4-6mm) punch biopsies of the skin to remove the small skin tracts to the cyst and removing the cyst and hair through these. Patients who have GIPS often experience a quicker recovery and seem to have a lower risk of wound complications. GIPS may not be suitable for all patients.
ALERT: Call your child’s doctor, nurse, or clinic if you have any concerns or if your child has special health care needs not covered by this information.
Wisconsin's highest-rated pediatric surgical center
Recognized by the American College of Surgeons, our Level I verification represents the highest level of recognition for hospitals that perform complex surgical procedures in newborns and children.
Make an appointment
To make an appointment, call our Central Scheduling team or request an appointment online.
